Production planning and control manages and schedules the allocation of human resources, raw materials, work centers, machinery, and production processes. It finds the most efficient way to produce finished goods with the lead times needed to meet production demand. Production planning and control are two strategies that work cohesively in manufacturing. Planning involves what to produce, when to produce, how much to produce, and more. Production control ensures optimum performance from the production system by using different control techniques for better throughput targets.
What is production planning?
Production planning helps manufacturers work smarter by efficiently managing internal resources to meet customer orders or demands. It solves what, when, and how much to produce. It establishes production capacity and identifies what raw materials, bill of materials, or alternate bill of materials are needed to meet demand. Then it prepares a workable production plan.
What is production control?
Production control monitors production and measures performance, providing visibility and reporting. If any corrective action is needed, it gets initiated with production control. It includes different control techniques to achieve optimal levels of production performance.
What are the objectives of production planning and control?
The overall objectives of production planning and control are to:
- Optimize resources and the scheduling of resources to meet production demand
- Ensure an efficient schedule
- Have resources ready when needed
- Keep inventory at optimal levels
- Increase productivity of internal resources (people, work centers, machines, tooling, etc.)
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Ensure the right person gets assigned to specific processes
- Coordinate with other departments (sales, customer service, purchasing, etc.)
Production planning and control is the core of any manufacturing unit. It includes material forecasting, master production scheduling, long-term planning, demand management, and more. The planning process kicks off with demand forecasting of a product. Using that forecast data and the internal resources available, the production plan is created.
Production planning and control is a strategy to plan a chain of operations that supports manufacturers to be at the right place and time. It helps them achieve the most efficiency from their resources. It also includes activities of other departments, such as sales, marketing, and procurement.
What are the benefits of production planning and control?
Some of the many benefits to production planning and control include:
- Optimized manufacturing capacity – ensures machines and employees work to capacity. That keeps costs down, increases efficiency, and provides greater profitability. It helps to identify areas of improvement and to plan for growth.
- Reduced inventory costs – allows manufacturers to only hold the necessary inventory. The software can predict demand and have a Just-in-Time scheduling strategy. Without a surplus of inventory, costs are kept low.
- On-time deliveries – helps to ensure production optimization and prompt deliveries. Getting products to their destination on time improves customer satisfaction. That increases customer retention and referrals.
- Better procurement of materials – shows when materials should get purchased for production. Having this information helps to know when to order and what is needed to meet customer and production demand. Knowing when to order lets procurement buy in advance to find the best deal. This also helps to save money and improves relationships with suppliers.
- Streamlined production processes – ensures that materials and internal resources for production are ready when needed and shows what capacity is available, and when. This keeps production running smoothly. It also helps employee satisfaction as it eliminates frustration from interruptions in production and workflows.
- Minimal resource waste – eliminates material shortages or surpluses for less resource waste. This lessens employee time wasted. Capital is not tied up in inventory that is not used. There is less production waste because delays that cause discarded materials get eliminated.
What is the role of production planning and control in manufacturing?
Production planning and control ensures the resources for production are ready when needed. Materials, equipment, and labor must be available at the right time to optimize production. It is the central part of a manufacturing business. The larger a business gets, the more PPC becomes essential for a smooth-running operation.
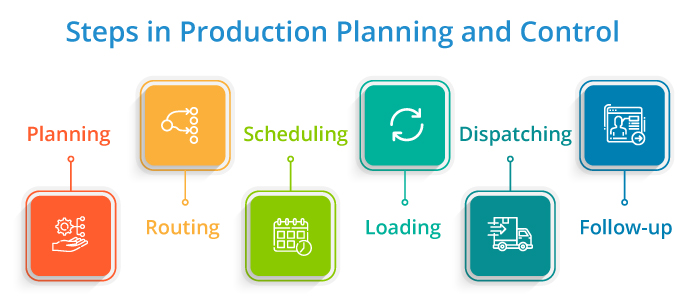
What are the steps in production planning and control?
1. Planning
Planning determines what will be produced, by whom, and how. It formulates the plan for labor, equipment, work centers, and material requirements needed for production.
Relevant information from various sources helps to develop a production plan. For instance, data from sales on order quantities and promised delivery dates. Product specifications from the engineering department may also be needed. The planning step helps to keep a streamlined approach to the production process.
2. Routing
Routing determines the path raw materials flow within the factory. Using the sequence, raw materials are transformed into finished goods.
Coordinating every production process and scheduling every step is important to measure the production process duration. Routing shows the quantity and quality of materials and resources needed. It also shows the operations used and the place of production.
Routing manages the “How”, “What”, “How much”, and “Where” of production. It systematizes the process and optimizes resources for the best results.
3. Scheduling
Scheduling emphasizes “when” the operation will be completed. It aims to make the most of the time given for the completion of the operation.
As per Kimball and Kimball, the definition of scheduling is –
“The determination of the time that should be required to perform the entire series as routed, making allowance for all factors concerned.”
Organizations use different types of schedules to manage the time element. These include Master Schedule, Operation Schedule, Daily Schedule, and more.
4. Loading
Loading looks into the amount of work loaded against machines or workers. The total time to perform new work is added to the work already scheduled for the machine or workstation.
If a machine or workstation has capacity available, more orders can make up the underload. If there is a capacity overload, proactive measures can prevent bottlenecks. Adding a shift, requesting overtime, bringing in operators from another shop, or using a sub-contractor are possible options.
5. Dispatching
Dispatching is the release of orders and their instructions. It follows the routing and scheduling directions. This step ensures all items are in place for the employees to do their jobs.
Here are the points that are part of “Dispatching”:
- Issue materials or fixtures that are important for production
- Issue orders or drawings for initiating the work
- Maintain the records from start to finish
- Start the control procedure
- Cascade the work from one process to another
6. Follow-up
Also known as expediting, follow-up locates fault or defects, bottlenecks, and loopholes in the production process. In this step, the team measures the actual performance from start until the end and then compares it with the expected performance.
Areas that have problems, must get addressed. Follow-up gets to the root of the issue and helps resolve it. For instance, if schedules are not met, is it from an unusual circumstance? Or is it something that needs to get adjusted? The production manager may need to revise production targets, loads, or schedules to correct the issue.
Types of Production Planning
1. Master production schedule
A Master production schedule is a plan that tells when the production will begin for what products, at what time, and in what quantities. The purpose of a master production schedule is to create a realistic plan to ensure on-time delivery of goods while minimizing overstock.
2. Materials requirement planning
Material requirement planning ensures availability of raw materials, maintains the lowest possible stock level, promotes inventory control, and helps plan purchasing activities.
3. Capacity planning
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by the organization to meet customers’ orders and changing demand for the product. It aims to strike a balance between expenses and resources as well as demand and supply.
4. Workflow planning
Workflow planning is planning a sequence of operations performed during the production process. It allows you to track each item’s work and see who is responsible for the task and its completion. In other words, workflow planning helps check the status of the task.
Production Planning Tools
Manufacturers rely on multiple tools to prepare the production plan and track progress such as charts, spreadsheets, or visualization software, etc. Instead of investing in multiple tools, a single ERP solution can help you plan production and use production control strategies to ensure that the plant floor is performing well and deliveries are on time.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software offers real-time visibility that helps decision-makers understand variances, eliminate waste, ramp up production, and improve transparency within the organization. ERP makes updating a job’s status easy as it can be done on mobile devices without leaving the workstation.
Benefits of ERP in production planning
Modern ERP ensures automated workflow which eliminates repetitive tasks such as data entry. ERP helps manufacturers plan, execute, and control production while integrating these operations into other business processes.
ERP has inbuilt Material Requirement Planning functionality which ensures minimum stock and risk for holding extra inventory. It ensures efficient and streamlined manufacturing processes.
How does OptiProERP help manufacturers with production planning and control?
OptiProERP is a manufacturing ERP natively embedded on SAP Business One, the leading platform for small and midsize enterprises. It provides a complete view of resource capacity, backlogs and bottlenecks, plant floor data, and inventory demand all in a single system.
Contact us if you want to learn how OptiProERP can help in planning production activites to increase your efficiency and profitability.
Follow Us