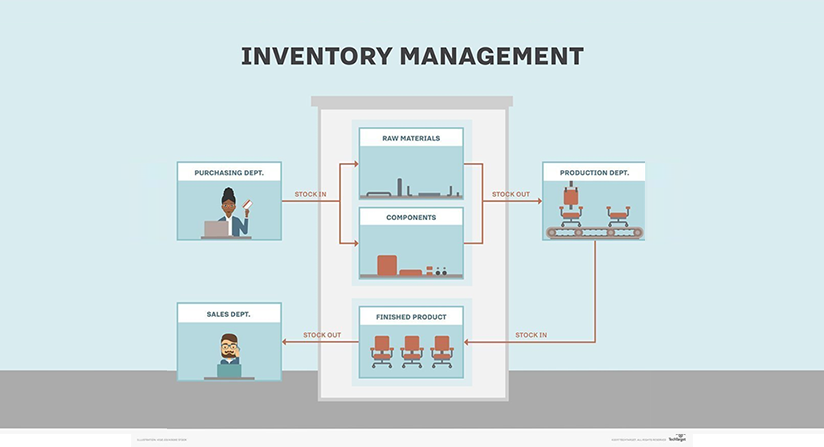
In this tech-driven world, data is the driving force for every business, many of which use Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. ERP software is a complete business management suite integrating data and business functions across sales, finance, accounting, purchasing, production, and other departments.
Digital data stored in ERP gives cybercriminals a significant opportunity. Ransomware attacks have grown by 13% in the last five years, with an average cost of $1.85 million per incident. In the coming year, cybercriminal activities are expected to further escalate by extortion tactics. There is the threat of encryption of the victim’s data, and if they don’t pay the ransom, their data can be leaked or sold.
What is ERP security, and how does it matter?
ERP systems house critical and confidential business data, so robust security algorithms and measures are necessary to safeguard sensitive data. Tech-savvy criminals know the weak points to breach systems. Therefore, businesses must regularly run vulnerability assessment audits or tests to find any underlying entry points.
Challenges in modern ERP security
ERP software hosts vast amounts of sensitive data such as customer information, supply chain details, property information, accounting transactions, etc. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats pose a significant risk to ERP data integrity. Below are the challenges manufacturers face in maintaining modern ERP security.
1. Shared responsibilities
Distributing cyber security roles and responsibilities across your business departments is crucial to ensuring your ERP security strategy is successful. For example, ERP providers add a new dimension to security strategy, giving employees the authority to implement controls for data that flows in and out of the ERP system.
2. Authorization issues
Human resources and IT departments are often hurrying to onboard new users as quickly as possible, leading to a lack of stringency while handing out ERP authorizations. This also happens in the case of an employee leaving the company. To combat this challenge, manufacturers should focus on the in-built provisioning and authentication capabilities and automated workflows supporting authorization.
3. Inadequate knowledge about security
Circulating a memo with your official phishing policy won’t educate employees about ERP security. You should have regular training sessions with your teams and make them aware of the risk of weak passwords and poor security protocols. Make sure that cyber security trainers are knowledgeable about phishing tactics, and they prioritize ERP security above everything.
4. Data export
Despite having every process and data online, users download and save spreadsheets for offline use. This again remains one of the growing challenges regarding ERP security and cybercrime. Companies should restrict employees from downloading files by tracking user actions, and they should limit access to vulnerable business data. Cloud ERP has integrated security features that can be automated. It notifies you of unauthorized access to data.
5. One-factor authentication
Only 38% of large organizations use multi-factor authentication to protect their accounts. One-factor authentication means having a single password or passcode. Organizations must implement two-factor authentication (2FA), including security tokens and biometric scans.
Statistics regarding ERP security
- 136 manufacturing/utility businesses suffered data breaches in the year 2022.
- The global average data breach cost in 2023 was USD 4.45 million, a 15% increase over the past three years.
- By 2026, Gartner predicts that 60% of organizations will shift from external hiring to “quiet hiring” from internal talent markets to address systemic cyber security and recruitment challenges.
- Through 2026, more than 40% of organizations, including two-thirds of midsize enterprises, will rely on consolidated platforms to run cyber security validation assessments.
- The average cost of a data breach in the manufacturing industry is $38 million, according to Accenture.
How on-premise and cloud ERP systems security differs
On-Premise ERP Security:
Control and Customization:
Advantage: Organizations have direct control over every aspect of security, allowing them to tailor security measures to their specific needs.
Challenge: This control also means that the organization is responsible for implementing, maintaining, and updating security measures, requiring a skilled IT team.
Physical Security:
Advantage: Physical access to servers is restricted to the organization’s premises, providing a higher level of control over physical security.
Challenge: Organizations need to invest in robust physical security measures for their data centers to prevent unauthorized access.
Data Isolation:
Advantage: Since data resides on-premise, organizations have a direct view and control over data isolation measures.
Challenge: Implementing and managing data isolation requires careful configuration to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Network Security:
Advantage: Organizations can implement and customize their network security protocols, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Challenge: Regular monitoring and updates are crucial, and organizations must stay vigilant against evolving cyber threats.
Upgrades and Patching:
Advantage: Organizations have the flexibility to schedule and control the application of updates and patches.
Challenge: Delayed or neglected updates can lead to vulnerabilities, and organizations bear the responsibility for timely maintenance.
Cloud ERP Security:
Provider Security Measures:
Advantage: Reputable cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures, often surpassing the capabilities of individual organizations.
Challenge: Organizations must trust the provider’s security practices and ensure that they align with regulatory and compliance requirements.
Data Encryption:
Advantage: Cloud providers typically implement strong encryption for data in transit and at rest, ensuring a high level of security.
Challenge: Organizations need to understand and trust the provider’s encryption standards and practices.
Physical Security of Data Centers:
Advantage: Cloud providers invest in state-of-the-art physical security for their data centers, including surveillance, access controls, and environmental controls.
Challenge: Organizations have limited visibility into the physical security measures of the provider’s data centers.
Automatic Updates and Patches:
Advantage: Cloud providers often handle updates and patches automatically, reducing the burden on organizations and ensuring timely application.
Challenge: Organizations may have less control over the timing and testing of updates, potentially impacting customization.
Shared Responsibility Model:
Advantage: Cloud providers follow a shared responsibility model, where they handle infrastructure security, and organizations are responsible for securing their data and user access.
Challenge: Organizations must understand and fulfill their responsibilities within the shared model to ensure comprehensive security.
Best practices to overcome ERP security challenges
The following are the ERP security best practices that can help you gain the most from the services related to ERP software:
1. Get educated about your ERP features and limitations
ERP is a complex business management solution. It is good if you can leverage the ERP’s built-in features to safeguard data against malicious vectors. If your ERP system is capable of providing security features, then you should definitely make sure to utilize such features and add an extra layer of protection against cybercrime attacks.
2. Third-party audits
If you periodically review your ERP vendor’s security posture and risk mitigation control practices, it will pressure the ERP vendor to invest in data security and protection.
3. Employee training and awareness
Regular training sessions about cyber security can help mitigate the risk of insider threats. Awareness programs help employees discover potential security threats and maintain a secure ERP environment.
4. Encryption and data masking
Encrypting data in transit and at rest adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Data masking techniques can obscure sensitive information, allowing users to perform their roles without exposing critical details.
Conclusion
With robust security algorithms and processes, ERP software can store and safeguard all your confidential data while maintaining and processing it. Cybercriminals know that ERP software has the organization’s valuable data and thus try to check out the organization’s weak points. Therefore, businesses must ensure the ERP security system’s protocols protect data from unwanted breaches.
Follow Us