Quality management is used by organizations to ensure a product or service is consistent and meets certain standards. It is made up of four segments: quality planning, quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvements.
What is Quality Management?

What is Quality Management?


What Are the Different Quality Management Methods?
There are four main quality management methods as noted below. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the right method depends on the organization’s structure, needs, and overall goals.
Standardized Systems
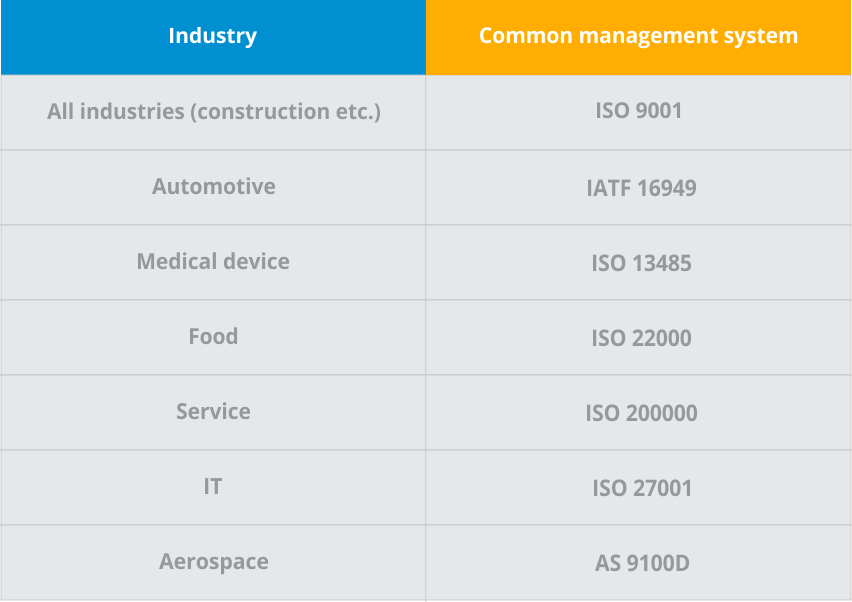
The federal government sets up standards, such as ISO certifications, that some organizations must follow according to the type of goods they produce (such as baby car seats.) Some businesses may not be required to use standards but do so anyway, as it helps their reputation or it aligns with their company’s objectives.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
When a company uses TQM, they want to improve quality across the organization. It takes into consideration the company’s overall quality goals and then looks at every process and other factors that affect quality to make positive change.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a very structured and data-driven method for quality management. Its focus is to define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. It is often used by large product manufacturers and requires intense training.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
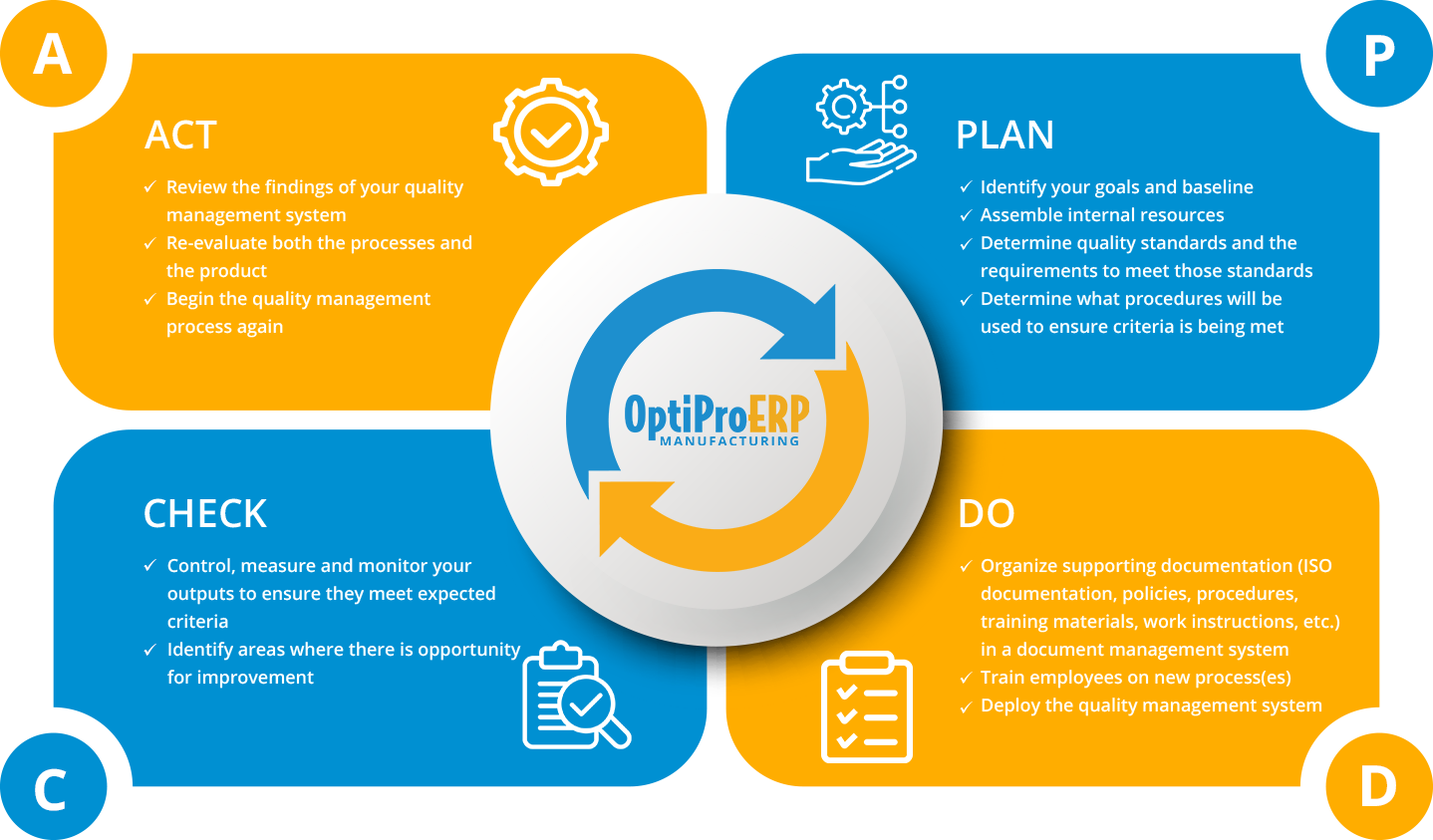
This method is just as the name indicates, it’s continuous. There is always room for improvement, and the business seeks to perfect its quality. CQI considers teams and individuals and how they impact quality. It includes Plan, Do, Check, and Act as its approach to quality, with people over processes being the focus.

What is a Quality Management System?
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a scheme of processes with the goal of making sure products are manufactured without any quality issues. It checks before, during, and after production to be sure all components and the final product meet industry and government regulations.
A quality management system can be handled manually, or with a software solution. It is broken down into two sections: quality assurance and quality control. Quality assurance is the act of carrying out inspections along the manufacturing process. Quality control includes inspections that help ensure customer expectations and industry standards are met – for example, by receiving feedback from customers, or conducting an inspection on the plant floor. Quality assurance is making sure your quality levels are met as the products are made, and quality control tests products after they are manufactured.

A quality management system can be handled manually, or with a software solution. It is broken down into two sections: quality assurance and quality control. Quality assurance is the act of carrying out inspections along the manufacturing process. Quality control includes inspections that help ensure customer expectations and industry standards are met – for example, by receiving feedback from customers, or conducting an inspection on the plant floor. Quality assurance is making sure your quality levels are met as the products are made, and quality control tests products after they are manufactured.

What Does the Quality Management System Do?
A quality management system should review products and their components throughout the production lifecycle, from receiving raw materials, to components in the WIP stage, to shipping the finished goods. The system will review how many products are made and determine if any were faulty. It should keep track of vendor products to ensure they meet quality standards – and if they don’t, they can be promptly returned. The system has inspection plans that examine people, products, and equipment.
A good quality management system will track any errors, keep an audit trail, find ways to correct any immediate problems, and fix anything needed to prevent future issues. It should be able to evaluate suppliers’ ability to deliver using key performance indicators (KPIs). A quality management system should keep track of any changes to policies and procedures as well as provide reports on anything related to the quality management process.

What Is the Role of a Quality Management System?

A quality management system’s role is to maintain the integrity of the company’s products so as to maintain a good reputation with customers. It’s a proactive measure to keep quality levels high and to ensure they meet or surpass regulatory, industrial, and customer standards.
QMS has the important role of providing manufacturers with a structure for tracking everything related to quality. When a good quality management system is in place, manufacturers feel more confident about their products. It helps them to define problems and inspect issues. In this way, manufacturers better control their processes, collect data, and analyze costs, problems, performance, etc.

QMS has the important role of providing manufacturers with a structure for tracking everything related to quality. When a good quality management system is in place, manufacturers feel more confident about their products. It helps them to define problems and inspect issues. In this way, manufacturers better control their processes, collect data, and analyze costs, problems, performance, etc.

What Is the Difference Between Quality Control and Inventory Control?
Quality control is in place to ensure that standards are met by measuring quality levels and output. Quality control helps to keep manufacturers compliant with industry and regulatory standards by measuring metrics against the standards set. It plays an important role in maintaining a business’s reputation.
Inventory control helps to maintain optimized levels of materials and products on hand for manufacturers to minimize waste and identify damaged inventory at the source. Inventory control keeps processes streamlined and locates any problem areas. By identifying problems and keeping quality stock readily available, inventory control supports the quality control process.

Why Is a Quality Management System Needed?
A quality management system is needed to ensure manufacturers’ products consistently meet customer expectations. It provides an audit trail of all quality-related actions, which is helpful for your defense in case of litigation. A quality management system keeps track of customer feedback, issues, suppliers, documentation, risks, training records, equipment used, audits, and inspections.
The importance of Quality Management System resides in its potential to identify production issues, eliminate unnecessary steps in the process, and close gaps in performance, which in turn improves processes for lean manufacturing. Quality management systems are important to comply with ISO standards and develop a corporate culture geared toward quality.

The importance of Quality Management System resides in its potential to identify production issues, eliminate unnecessary steps in the process, and close gaps in performance, which in turn improves processes for lean manufacturing. Quality management systems are important to comply with ISO standards and develop a corporate culture geared toward quality.

Who Needs a Quality Management System?
All manufacturers need a quality management system to make sure their products meet customers’ expectations. A quality management system also helps ensure responsibilities, schedules, relationships, contracts, and agreements are on par with industry standards.
A quality management system is important for manufacturers to manage their processes, keep all quality-related information in a central place, and document the controls in place, all with a view to improving collaboration between teams. It also helps to keep companies audit-ready, improves profits by eliminating errors and waste, lowers costs, increases performance, notifies suppliers quickly if their products are faulty, and maintains a culture of quality.

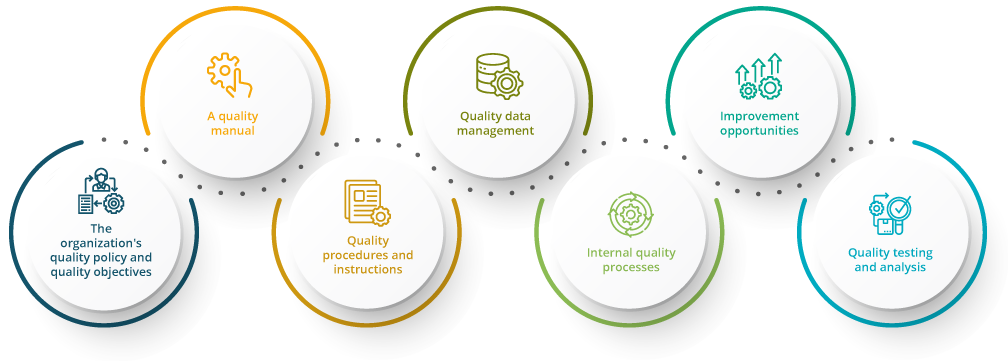
What Are the Key Components of a Quality Management System?
The key components of a quality management system are as follows:

What Are the Benefits of a Quality Management System?
There are many benefits to using a quality management system. Below is a list of the most significant benefits.
Greater Efficiency
With a quality management system, you gain control over processes to make them more streamlined and efficient.

Increased Profitability
A quality management system helps to increase profitability by increasing the number of satisfied customers and making improvements to operations that help lower costs.

Improve Quality
Improve processes to reduce errors, remove substandard raw materials, incorporate controls, and increase accountability.
Reduce Costs
Eliminate costs associated with scrapped finished goods and reworked goods.

Meet Compliance Standards
With strict controls in place, manufacturers can meet both government and industry standards.
Enhanced Reputation
By consistently providing quality products, manufacturers gain a solid reputation that retains existing customers and attracts new ones.

Better Collaboration
With coordinated processes and a single source of quality data, businesses with a good quality management system break down data silos and enjoy greater collaboration.

Greater Customer Satisfaction
Manufacturers with a quality management system produce high-quality products that satisfy customers.

What Are the Benefits of a Quality Management System with ERP?
Reduce IT Needs
With an ERP system, the operations of every department in your organization are integrated into one system. Thus, IT doesn’t have multiple systems to maintain, which results in lower costs.
Save Time
Since everyone is working from one system, data entry is simplified and errors are reduced. Everything resides in a single database so users have the latest information, updated in real time. All of this allows employees to work more efficiently.
Improve Accuracy
Gain better accuracy by eliminating manual data entry and automating processes. Not having to re-enter data into separate systems also reduces mistakes.
Increase Visibility
An ERP system works across the company so you have visibility into all departments. Sales can see what is happening with manufacturing, and procurement can see when inventory is running low. Everyone can work smarter and more efficiently. It also allows users to drill down into data to examine things closely. By having a greater quantity of data, better insight into company operations is achieved.

Simpler to Upgrade
When you only have one system to upgrade, it is much simpler than having multiple systems that may not integrate, or if they do, it is usually problematic when one or more needs to be upgraded. With ERP, all data is in a single database so it is easy to back up and incorporate back in once an upgrade is complete.
Greater Data Integrity
Due to increased accuracy and connectivity between departments, ERP provides greater data integrity. Since everything is stored in a single database and updated in real-time, you can count on the information being correct.

What Are the Features and Functionality of a Quality Management System?
A good quality management system should include the following functionality:
End-to-end Quality Control
The system should be set up to quickly identify and resolve issues in receiving, production, and shipping.
Work Center Tracking
Know how much was produced per work center and if there were any quality problems.
Material Review Board
This function tracks raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods to help procurement get the best deals and to quickly return supplies that are defective.
Mobile Data Collection
Capture quality control information from anywhere using mobile devices, or the web.
Return to Vendor
See when received goods are faulty so you can get them back to the supplier quickly.
Inspection Plans
Use quality control inspection plans, checklists, and tests to check people, products, and equipment.
NC and CAPA
Be able to track and keep an audit trail of non-conformances as well as corrective and preventative action processes.
AQL and RQL Sampling
Carry out 100% inspection or sampling routines for Accepted Quality Levels (AQL) and Rejectable Quality Levels (RQL) throughout processes.
Traceability and Recall Reporting
Implement forward and backward tracing of all movements of a serial or lot number.
Vendor Performance Evaluation
Use KPIs to report on how well vendors are performing.
Document Control
Document internal controls, security, and quality measures, as well as document searches and retrievals for audits or inspections.
Change Management
Receive multi-level notifications and historical tags with automated changes to policies, procedures, and more.

What Are the Key Types of Quality Management Systems?
Startup companies often use a manual method for quality management which can become difficult to sustain as they grow. There are also stand-alone quality management systems, as well as ERP systems that include quality management as a module.
When a quality management system is part of a manufacturing ERP system, it can fully manage and streamline your quality management and compliance processes throughout your supply chain, from purchasing and receiving to production and shipping.

What Is the Difference Between a QMS and an ERP System?
A quality management system manages only the quality control and assurance processes within a company. An ERP system, by contrast, has modules that handle departmental operations and work together with the quality management module. The whole organization can collaborate to ensure products and processes are of the highest quality.

What Are the Benefits of a QMS Integrated with ERP?

End to End Quality Control
When a quality management system is integrated with ERP, it allows the whole organization to be quality-focused. Capturing and coordinating information accurately ensures you’re continually meeting quality and regulatory standards. ERP helps to unify processes, better coordinate workflows, and improve the sharing of data to break down silos.


Supply Chain Optimization
A QMS in ERP lets you streamline post-inspection processes to quickly determine when received goods are faulty. You can set up automated audits and checks of incoming raw materials to ensure they meet the agreed-upon quality standards. It also analyzes supplier performance to make better decisions and reduce costs. ERP that is integrated with shipping, barcode, and RFID technology lets manufacturers track the movement of goods across the supply chain.


Real-time Data
Improve the speed and accuracy of data collection and quality management. Capture and evaluate inspection and QC test results from the shop floor or warehouse in real-time and have visibility from anywhere at any time. Being able to stop production due to a quality issue before or early into production instead of further down the line provides big cost savings and reduces frustrations.


Reduce Complexity
Manage processes, data collection, along with preventive and corrective actions easily in one system. With real-time tracking and insights, manufacturers can manage complex supply chains to ensure the quality of goods always meets the standards set.
Staff Collaboration
ERP provides a single system to fully manage and streamline your quality management and compliance processes throughout your supply chain, from purchasing and receiving to production and shipping. Quality is important across the organization and with ERP software, staff can easily collaborate, as they are all working with the same information from a single database.
Lower IT Costs
ERP cuts down on IT costs, since there is only one platform to maintain instead of multiple disparate solutions. When it is time to upgrade, it can be very challenging if there are many stand-alone systems integrated together. Data must be backed up from each system before the upgrade. Afterward, trying to get them all to work together again can be very time-consuming.


End to End Quality Control
When a quality management system is integrated with ERP, it allows the whole organization to be quality-focused. Capturing and coordinating information accurately ensures you’re continually meeting quality and regulatory standards. ERP helps to unify processes, better coordinate workflows, and improve the sharing of data to break down silos.


Supply Chain Optimization
A QMS in ERP lets you streamline post-inspection processes to quickly determine when received goods are faulty. You can set up automated audits and checks of incoming raw materials to ensure they meet the agreed-upon quality standards. It also analyzes supplier performance to make better decisions and reduce costs. ERP that is integrated with shipping, barcode, and RFID technology lets manufacturers track the movement of goods across the supply chain.


Real-time Data
Improve the speed and accuracy of data collection and quality management. Capture and evaluate inspection and QC test results from the shop floor or warehouse in real-time and have visibility from anywhere at any time. Being able to stop production due to a quality issue before or early into production instead of further down the line provides big cost savings and reduces frustrations.


Reduce Complexity
Manage processes, data collection, along with preventive and corrective actions easily in one system. With real-time tracking and insights, manufacturers can manage complex supply chains to ensure the quality of goods always meets the standards set.


Staff Collaboration
ERP provides a single system to fully manage and streamline your quality management and compliance processes throughout your supply chain, from purchasing and receiving to production and shipping. Quality is important across the organization and with ERP software, staff can easily collaborate, as they are all working with the same information from a single database.


Lower IT Costs
ERP cuts down on IT costs, since there is only one platform to maintain instead of multiple disparate solutions. When it is time to upgrade, it can be very challenging if there are many stand-alone systems integrated together. Data must be backed up from each system before the upgrade. Afterward, trying to get them all to work together again can be very time-consuming.

How Do You Choose the Right Quality Management System?
There are lots of options out there for QMS and ERP systems, so how do you choose the right one? Below are some of the key criteria to consider.
Industry Experience
Does the company have much experience in your industry? What other companies similar to yours have they worked with? Can they provide references? Can they speak knowledgeably about the quality requirements your company must meet? You’ll want to feel confident that not only can the software meet your needs, but that the people who will be providing the installation and training have industry knowledge.

Functionality Needs
You’ll want to understand what the software can do to determine if it will meet the needs of your business. For instance:
- Does it provide the quality compliance requirements necessary for your industry?
- If needed, can it easily integrate with your other system(s)?
- Does it track all non-conformances and provide a full audit trail?
- Does it offer Correct and Preventative Action management or CAPA that gets to the root cause analysis of a problem and helps you take corrective actions?
- Does it provide AQL (Acceptable Quality Limit) and RQL (Rejectable Quality Level) sampling throughout processes?
- Does it provide Document Control to record all of your quality activities?
- Does it display KPIs to help you understand how well suppliers are performing?
- Does it collect data from anywhere using mobile devices or the web?

Visibility
It’s important to have good visibility of key quality events in real-time to resolve issues proactively. You’ll want to be able to see what is happening across the business so you can truly understand issues. You should be able to monitor vendor performance and employees to see if they are compliant or if they need additional training.


Get a Fully Integrated QMS and ERP solution with OptiProERP and SAP Business One
OptiProERP is a complete manufacturing ERP solution embedded into SAP Business One. It provides business and manufacturing functionality, including robust quality management features. OptiProERP is mobile-friendly and cloud-based. It provides demand forecasting, IoT integration, machine learning, and AI. OptiProERP also includes e-commerce and warehouse management modules.
See OptiProERP’s Best-of-Breed Solution in Action





